HS is a complex disease driven by immune system dysregulation, with multiple proinflammatory cytokines contributing to its pathogenesis.1 The clinical presentation may also vary from person to person, making it challenging to manage.2,3
While current treatments like conventional systemic therapies (eg, antibiotics, retinoids) and surgical interventions offer some relief, they do not address the inflammatory drivers of HS.4,5

Currently approved biologics target specific cytokines such as TNF-alpha and IL-17 to address inflammation.5
In addition to TNF-alpha and IL-17, there is a range of proinflammatory cytokines involved in the pathophysiology of HS.6
Cytokines and signaling factors involved in HS pathogenesis6
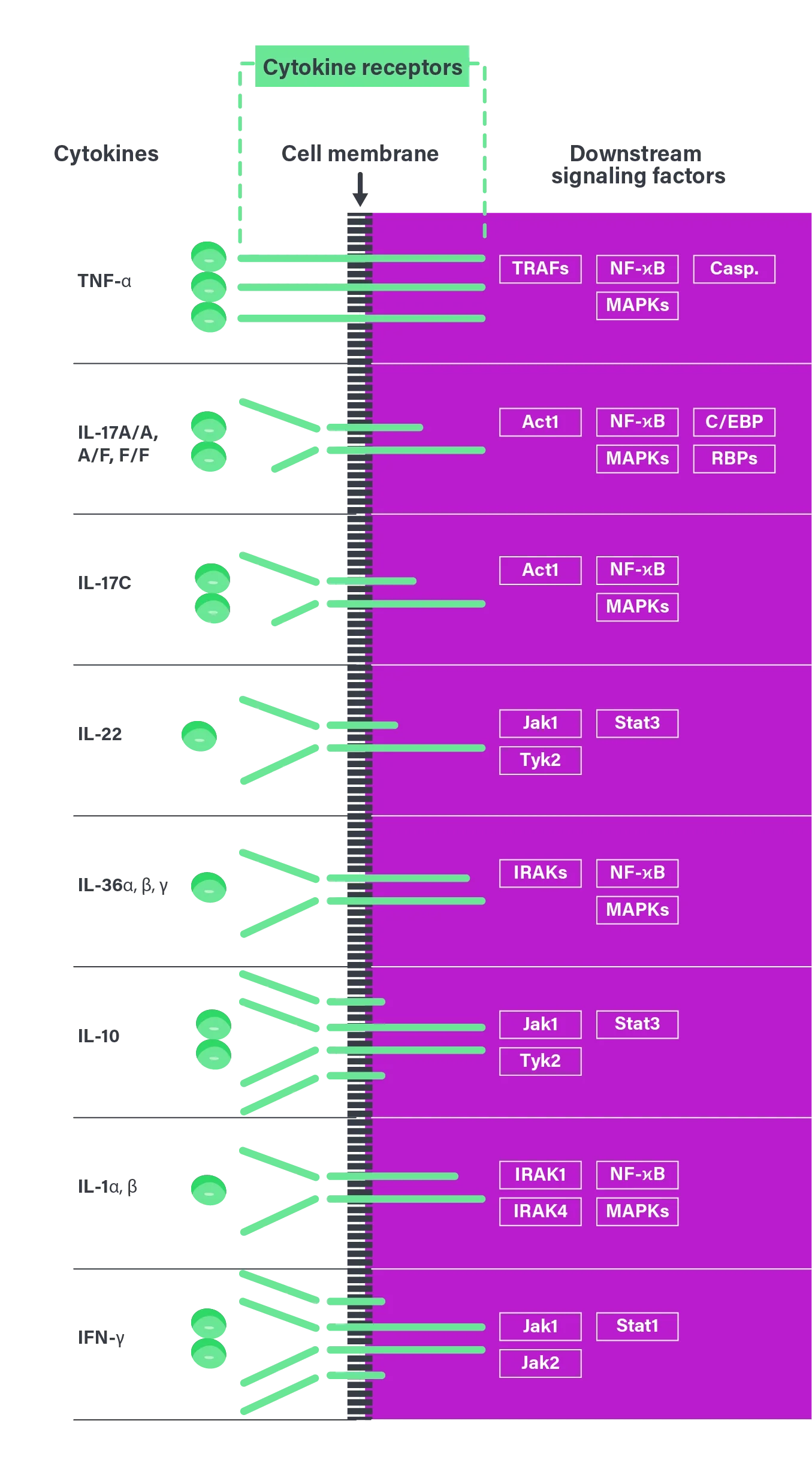
Proinflammatory cytokine signaling is mediated through the JAK-STAT pathway. Further understanding of this mechanism may help to inform the overall management of this complex condition.6,7
Learn how Incyte is committed to raising awareness for HS
Act, Act1 adaptor protein; Casp., Caspases; C/EBP, CCAAT/enhancer‑binding proteins; HS, hidradenitis suppurativa; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; IL, interleukin; IRAK, interleukin‑1 receptor‑associated kinase; JAK‑STAT, Janus kinase–signal transducer and activator of transcription; MAPK, mitogen‑activated protein kinase; NF‑ϰB, nuclear factor kappa B; RBP, RNA‑binding protein; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TRAF, TNF receptor–associated factor; Tyk2, tyrosine kinase 2.
REFERENCES: 1. Krueger JG, Frew J, Jemec GBE, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: new insights into disease mechanisms and an evolving treatment landscape. Br J Dermatol. 2024;190(2):149-162. doi:10.1093/bjd/ljad345 2. Ben Abdallah H, Bregnhøj A, Iversen L, Johansen C. Transcriptomic analysis of hidradenitis suppurativa: a unique molecular signature with broad immune activation. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(23):17014. doi:10.3390/ijms242317014 3. Zouboulis CC, Benhadou F, Byrd AS, et al. What causes hidradenitis suppurativa? — 15 years after. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29(12):1154-1170. doi:10.1111/exd.14214 4. Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: a publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations: part II: topical, intralesional, and systemic medical management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81(1):91-101. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.02.068 5. Sabat R, Alavi A, Wolk K, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Lancet. 2025;405(10476):420-438. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)02475-9 6. Wolk K, Join-Lambert O, Sabat R. Aetiology and pathogenesis of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183(6):999-1010. doi:10.1111/bjd.19556 7. Rumberger BE, Boarder EL, Owens SL, Howell MD. Transcriptomic analysis of hidradenitis suppurativa skin suggests roles for multiple inflammatory pathways in disease pathogenesis. Inflamm Res. 2020;69(10):967-973. doi:10.1007/s00011-020-01381-7

